Headaches can have various causes, ranging from mild and temporary to severe and chronic. Here are some common causes of headaches:
- Primary Headaches:
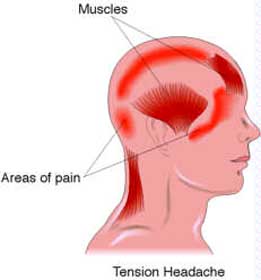
- Tension-Type Headaches: These are the most common type of headache and are often described as a dull, squeezing pain around the forehead or the back of the head and neck. Stress, poor posture, muscle tension, and eye strain can contribute to tension-type headaches.
- Migraines: Migraines are characterized by severe, throbbing pain, often on one side of the head, and are typically accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, sound, or smells, and visual disturbances. Migraines may be triggered by factors such as hormonal changes, certain foods, stress, lack of sleep, and sensory stimuli.
- Cluster Headaches: Cluster headaches are rare but extremely painful headaches that occur in cyclical patterns or clusters. They often occur on one side of the head and are accompanied by symptoms such as red or watery eyes, nasal congestion, and restlessness.
- Hemicrania Continua: This is a rare type of headache characterized by continuous, fluctuating pain on one side of the head. It may be accompanied by autonomic symptoms such as tearing, redness of the eye, and nasal congestion.
- Secondary Headaches:
- Sinus Headaches: Sinus headaches occur when the sinuses become inflamed due to allergies, infections (such as sinusitis), or other sinus disorders. The pain is typically localized to the forehead, cheeks, or bridge of the nose.
- Rebound Headaches: Also known as medication-overuse headaches, rebound headaches occur when overuse of pain medications, especially opioids, triptans, or combination analgesics containing caffeine, leads to a worsening of headache symptoms.
- Headaches Due to Trauma or Injury: Headaches can result from head trauma or injury, such as concussions, whiplash, or skull fractures.
- Cervicogenic Headaches: These headaches originate from the neck and are often caused by musculoskeletal problems or abnormalities in the cervical spine.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): High blood pressure can cause headaches, especially when it is severe or sudden.
- Infections: Headaches can be a symptom of various infections, including viral illnesses (such as the flu or common cold), bacterial infections (such as meningitis or encephalitis), and other systemic infections.
- Brain Tumors or Lesions: While rare, headaches can sometimes be a symptom of underlying brain tumors or other structural abnormalities in the brain.
- Other Causes:
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can lead to dehydration, which can cause headaches.
- Eye Strain: Prolonged use of digital screens, reading in poor lighting, or uncorrected vision problems can cause eye strain and headaches.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause, can trigger headaches in some individuals.
Best answer:
Answer by BitburgerPilsMan
Regular All kinds of Headache are caused by too much blood in the head. I suppose sex would, at least for the male population, since there would be a need for blood at the other head.
Add your own answer in the comments!