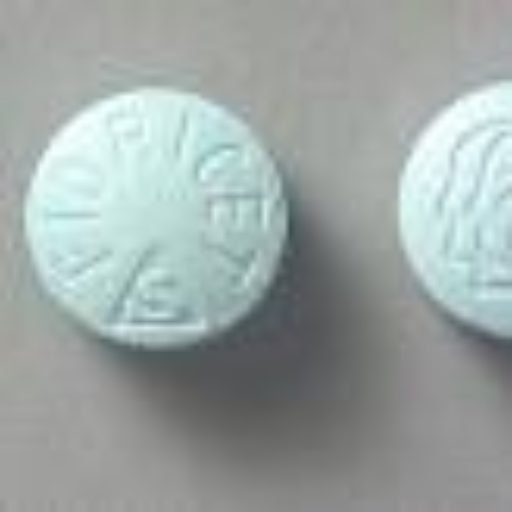
Low back pain can stem from various injuries, conditions, or illnesses, with the most common cause being damage to the muscles or tendons in the back.
The severity of pain can vary, ranging from mild discomfort to intense agony. At times, the pain can hinder mobility, sleep, work, or routine tasks.
Typically, rest, pain relievers, and physical therapy (PT) are effective in improving lower back pain. Cortisone injections and hands-on therapies, such as osteopathic or chiropractic manipulation, can alleviate pain and facilitate the recovery process. Surgical intervention may be necessary for certain back injuries and conditions.

How to Relieve Low Back Pain Naturally ?
Relieving low back pain naturally can be effective in managing discomfort and promoting healing. Here are some natural approaches and home remedies that can help alleviate low back pain:
- Rest: Give your back a break by resting in a comfortable position. Avoid activities that worsen the pain, but don’t stay immobile for too long, as gentle movement is important for recovery.
- Ice and Heat Therapy:
- Ice: Apply an ice pack to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day during the first 48 hours after the onset of pain. Ice helps reduce inflammation and numb the area.
- Heat: After the initial 48 hours, you can switch to heat therapy using a heating pad or warm compress for 15-20 minutes at a time. Heat relaxes muscles and increases blood flow, which can help with healing.
- Gentle Stretching and Exercise: Engage in gentle stretching exercises that target the lower back and surrounding muscles. Stretching can improve flexibility and relieve tension. Activities like yoga and tai chi may be beneficial.
- Take walks. Walking is a very safe and good exercise. Brisk walking at work or outside will help you to maintain a healthy weight and keep pressure off your back.
- Lift correctly. When you lift something heavy, it’s very easy to twist the wrong way. This can lead to muscle spasm and pain. Use proper body mechanics by engaging your leg muscles, not your back, when you pick up heavier items. Get help if the item is too much for you to lift alone.
- Watch your weight. Extra weight puts a strain on your back. In order to deal with extra weight, your spine can become tilted and stressed unevenly. The back may lose its proper support and develop an unnatural curvature of the spine over time.
- Strengthen Your Core Muscles: Building core strength can help support your spine and reduce the risk of future low back pain. Focus on exercises that strengthen the abdominal and back muscles, such as planks and bridges.Engaging in yoga is a highly effective approach for achieving a range of benefits for your back and overall musculoskeletal health. Yoga can aid in:
- Stretching Your Back: Yoga exercises are designed to gently stretch and lengthen the muscles and tissues in your back, promoting flexibility and relieving tension.
- Enhancing Muscles and Joint Health: Regular practice of yoga can improve the strength and stability of the muscles and joints in your back, leading to better support for your spine.
- Improving Blood Circulation: Yoga poses and movements encourage the circulation of healing nutrients throughout your body, aiding in the healing and maintenance of your back.
- Increasing Spinal Flexibility: Yoga is particularly effective in enhancing the flexibility of your spine, which can alleviate stiffness and promote better range of motion.
- Good Posture: Maintain proper posture when sitting, standing, and lifting objects. Avoid slouching or hunching, and use ergonomically designed chairs and workspaces if possible.It’s crucial to pay close attention to the health of your spine and hip joints and muscles. To prevent fatigue and reduce stress on these vital areas, consider following these simple tips:
- Limit Prolonged Sitting: Avoid sitting for extended periods of time, especially in positions that place pressure on your spinal discs. If possible, use a standing desk during work hours. Remember to take short breaks every hour, stand up, and walk a short distance to relieve the strain on your discs.
- Maintain Proper Posture: Be mindful of your posture throughout the day. Ensure that your neck, shoulders, and back are aligned correctly to minimize stress on your spine. Poor posture can contribute to various back problems, including pain and discomfort.
- Alternate Activities: Rotate your activities to prevent over-fatigue of specific muscles and joints. For example, if you’ve been standing and working for an extended period, consider switching to a seated task to give your muscles and joints a chance to rest and recover. You can return to a standing position once they’ve had an opportunity to relax.
- Sleep Support: Use a supportive mattress and pillows that promote proper spinal alignment while sleeping. Sleeping on your side with a pillow between your knees can help alleviate pressure on the lower back.To enhance your sleep quality naturally, consider trying these various sleep aids individually to determine which one suits you best:
- Vitamins C and B6: The body’s natural steroids play a vital role in regulating metabolism and promoting restful sleep. Supplements of vitamins C and B6 are recognized for their ability to support the production and regulation of natural steroid hormones.
- Melatonin: Melatonin, your body’s innate sleep hormone, can be taken as a supplement to improve your sleep-wake cycle and encourage better sleep patterns.
- L-theanine: This amino acid, present in tea leaves, has the potential to induce relaxation and contribute to improved sleep for some individuals.
- Valerian: Supplements derived from the root of the valerian plant are believed to facilitate quicker sleep onset and longer-lasting sleep, aiding in achieving a more restful night.
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Incorporate foods rich in anti-inflammatory nutrients into your diet. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, turmeric, ginger, and fruits and vegetables can help reduce inflammation and pain.Regularly indulging in these healthful drinks may contribute to alleviating your back pain.
- Turmeric Milk: Turmeric, an Asian spice, is brimming with antioxidant, anti-arthritic, and anti-inflammatory properties. A simple way to integrate turmeric into your diet is by mixing a small amount (1/2 teaspoon) of turmeric powder into a glass of warm milk. If you prefer a touch of sweetness, you can add honey or stevia to the milk. Consume this elixir, ideally just before bedtime, allowing the anti-inflammatory processes to work their magic as you sleep. For those who find dairy products to be inflammatory, opting for plant-based alternatives like almond milk can be a helpful choice.
- Tart Cherry Juice: Cherries are renowned for their wealth of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents. Cherry juice can provide relief from muscle pain, whether it’s chronic or exercise-induced. You can readily find cherry juice, often containing tart cherry extract, at grocery stores. Try incorporating a daily glass of cherry juice into your routine to assess its positive impact on easing your back pain.
- Ginger-Green Tea: Another option to explore is infused herbal beverages, like ginger-green tea. This delightful blend combines the pain-relieving properties of green tea and ginger. Ginger-green tea bags are readily available at grocery stores, offering you the convenience of savoring a cup either at work or in the comfort of your home.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration helps maintain the elasticity of spinal discs, reducing the risk of low back pain.
- Herbal Remedies: Some herbs and supplements, such as devil’s claw, white willow bark, and ginger, have anti-inflammatory properties and may provide relief. Consult a healthcare provider before using any herbal remedies or supplements, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or are taking medications.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress and muscle tension, contributing to pain relief.
- Massage Therapy: Regular massage therapy sessions from a qualified therapist can help relax muscles, improve circulation, and reduce tension in the lower back.
- Quit smoking. Smoking restricts blood flow to the discs that cushion your vertebrae. This could lead to quicker disc degeneration. Smoking also reduces calcium absorption and new bone growth.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and promote healing.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments can help realign the spine and improve joint function, potentially providing relief from low back pain.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get enough sleep each night to allow your body to heal and recover.Sleeping flat on your back puts pressure on your spine. Elevate your knees slightly by placing a pillow under them. If you’re a side sleeper, put a pillow between your knees to reduce pressure on your back.
- Warm Pool: Taking advantage of the buoyancy of water can provide numerous benefits, particularly when it comes to exercise and pain management. Here’s why exercising in water can be advantageous:
- Reduced Impact: The buoyancy of water significantly reduces the impact and stress on your joints and muscles compared to exercises on land. This makes it an excellent choice for individuals with conditions that cause pain or limited mobility.
- Pain Relief: Exercising in water can help alleviate pain by promoting muscle relaxation and reducing nerve sensitivity. The gentle resistance of water can also aid in strengthening muscles without causing excessive strain.
- Improved Circulation: Water therapy exercises can enhance circulation, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions like arthritis or chronic pain.
- Enhanced Flexibility: The natural resistance of water supports improved joint flexibility and range of motion, making it easier to perform exercises that may be challenging on land.
If you prefer warmer water temperatures, you can explore two options:
-
- Water Exercise Classes: Many fitness centers offer water exercise classes conducted in pools with temperatures around 83 to 88 degrees Fahrenheit. These classes often include a variety of exercises designed to improve strength, flexibility, and overall fitness while minimizing discomfort.
-
- Hydrotherapy Pools: Hydrotherapy pools are typically maintained at temperatures above 90 degrees Fahrenheit. These warmer pools are especially beneficial for individuals seeking relief from muscle tension, pain, and stiffness. Hydrotherapy sessions are often guided by therapists and may involve specific exercises and treatments.
20. Taking a Vitamin D3 Supplement : Supplementing with vitamin D3 can be beneficial for individuals with the approval and guidance of their healthcare provider. Vitamin D is crucial for several bodily functions, including bone health, neuromuscular function, and immune system support. Here’s how vitamin D3 supplementation may help reduce back pain:
-
- Calcium Absorption: Vitamin D plays a vital role in enhancing the absorption of calcium from the digestive system. Adequate calcium levels are essential for maintaining strong bones and preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
- Bone Strength: By improving calcium absorption, vitamin D contributes to the overall strength and health of bones. This can be particularly important in preventing or managing back pain caused by conditions like osteoporosis or vertebral fractures.